2024年1月29日,我校植物保护学院张金林教授团队在环境科学权威国际期刊Science of the Total Environment(中国科学院一区TOP,IF=9.8)上在线发表了题为“Establishment of an indirect competitive immunoassay for the detection of dicamba based on a highly specific nanobody”的研究论文,研究报道了一种基于纳米抗体进行环境中除草剂麦草畏检测的新方法,为该除草剂的合理安全使用提供技术支撑。我校植物保护学院农药系霍静倩副教授和张金林教授为共同通讯作者,论文第一作者是霍静倩副教授指导的2022级硕士研究生王雅森。研究工作得到国家自然科学基金(32102246,32272573),河北省自然科学基金(C2023204073),河北省重点研发计划项目(22326512D),河北省现代农业产业技术体系玉米创新团队(HBCT2023020201)和河北农业大学引进人才科研启动经费(YJ201963)的资助。


麦草畏是一种传统的高效低毒除草剂,近年来随着耐麦草畏转基因作物的开发而获得了新生。然而,麦草畏挥发性强,容易对敏感作物造成漂移药害。此外,麦草畏的残留还会影响水生生物的遗传毒性,造成DNA单链断裂。鉴于此,开发高效灵敏的检测方法对于现场监测环境中的痕量麦草畏及其漂移药害评估至关重要。本研究团队前期通过半抗原合理设计获得性能优异的麦草畏多克隆抗体(J.Agric.Food Chem.2019,67,5711-5719)。由于纳米抗体较传统抗体在稳定性和特异性等方面具有一定优势,且目前缺乏基于纳米抗体的麦草畏检测分析方法。在前期研究基础上,本研究论文通过对骆驼进行免疫和噬菌体展示文库构建等方法,成功获得了能够特异性识别麦草畏的纳米抗体,并构建了基于纳米抗体的间接竞争性免疫分析方法,IC50为0.93 μg/mL,线性范围为0.11~8.01 μg/mL。


Fig.1. (A) The best combination of immunogen and coating antigen used in this study; (B) The titer of camelid antiserum, the concentration of different coating antigens was 1 μg/mL; (C) Inhibition of free dicamba (1 μg/mL) to different concentration of camelid antiserum, hapten 24-OVA (with different concentration) was employed for coating antigen; (D) The standard curve of ic-ELISA based on polyclonal antiserum, with the IC50 value of 15.8μg/mL.
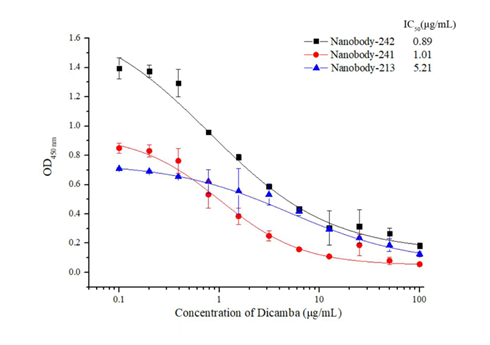

Fig. 2. Standard curve of ic-ELISA based on the isolated three nanobodies, with the IC50value of 0.89 μg/mL, 1.01 μg/mL, and 5.21 μg/mL, respectively; Standard curve for dicamba by ic-ELISA based on Nb-242. Serial dilutions of dicamba standard were mixed with Nb-242 in optimized buffer. Then 100 μL of the mixtures were added to the coating antigen-coated wells. Each point represents the mean value of three replicates.
本研究通过添加回收试验和实际样品检测试验对所构建的酶联免疫检测方法的精确度和适用性进行了评价。特异性试验结果同样表明,本研究中所构建的ELISA方法对麦草畏表现出较好的特异性。所开发的免疫测定与标准高效液相色谱法有很好的相关性。进一步证实了本研究中所构建的ELISA方法的适用性,对指导麦草畏的科学合理使用具有重要意义。
Table 1. Cross-reactivity of the Nb-242 and polyclonal antibody against dicamba structural analogs
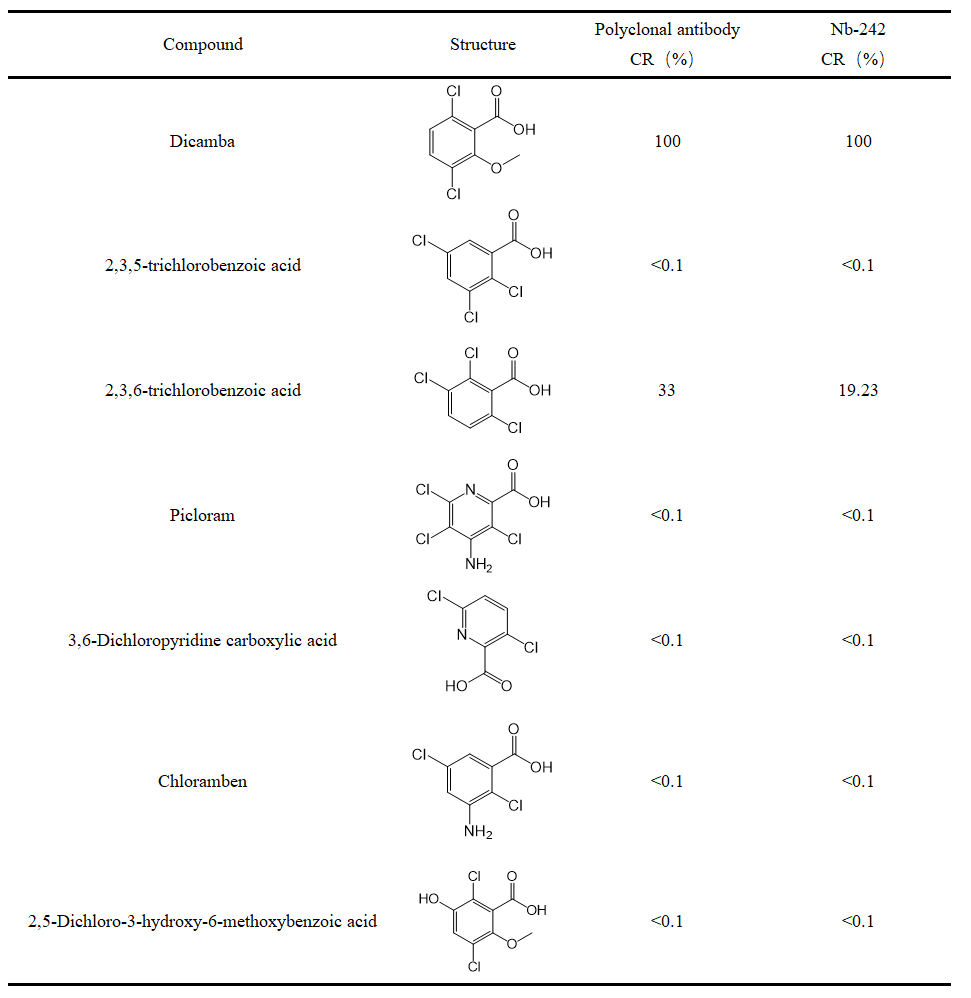
Table 2. Spike-recovery results for tap water and soil samples determined by ELISA and HPLC

另外,本研究基于获得的纳米抗体的氨基酸序列,利用计算机辅助技术进行了纳米抗体的同源模建并与麦草畏进行了分子对接,分析了两者之间的结合模式以及纳米抗体特异性识别麦草畏的关键氨基酸位点,为下一步纳米抗体的定向结构改造奠定重要基础。
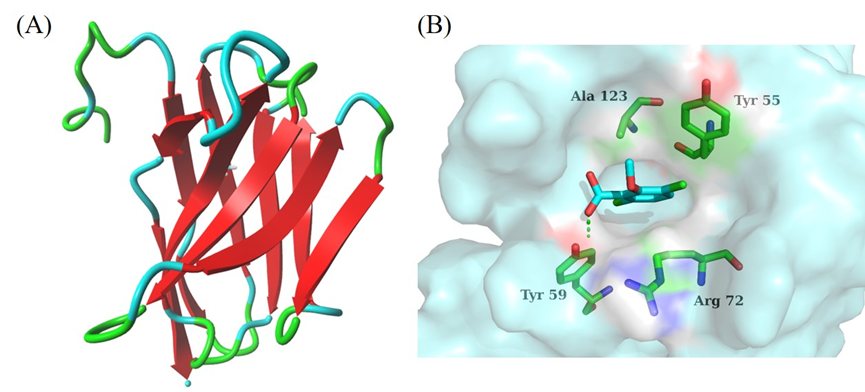
Fig. 3. The results of homologous modeling and molecular docking. (A) The three-dimensional structure of Nb-242 obtained by homologous modeling; (B) The recognition mode between Nb-242 and dicamba in 3D docking plot
